Linux is an amazing operating system in this present age. The most important benefit of this system is that it comes for free, and you can use any open-source software here. The use of the desktop system is wonderful, and its increased popularity has resulted in its professional use on different platforms. But often, as a Linux user, you will need to apply Linux Partition Manager for the smooth operation of your system. But, if you are a newbie, at times, it might become hard for you to use the Linux partition tool.
Best Linux Partition Manager Tools
There are a number of open source partition software available in the market. You can easily apply them to take care of your disk space and maintenance. Here are the best 8 Linux partition managers briefly described to help you through the process and smoothly manage your computer disks.
1. Fdisk – (Command Line)
If you want to manipulate your disk partition tables, Fdisk is one of the best produced so far. The software is more popular for its user-friendly command-line tool, while the other available sources are not as easy to use. The software comes with a few specific features.
There are multiple table formats. You are even enabled to use MS-DOS with this particular software. The text-based interface is really adorable. There are several options available with this one. The users are also allowed to exercise commands like resizing, deleting, and copy-and-paste options, which are available like the other times.
2. GNU Parted – (Command Line)
This is another impressive Linux partition tool for its simplicity. Among global Linux users, the tool is commonly known simply as ‘Parted.’ The software is mainly used for hard disk partitions, but you can manage your entire hard disk using this single tool.
The tool is enabled to ensure a smoother partitioning process. It supports multiple partition table formats and allows you to work with MS-DOS and other systems. GNU Parted also allows you to use some necessary and usual commands, such as deleting, extending, and even shrinking disk partitions. As a user, you can also locate the file system on it.
3. Gparted
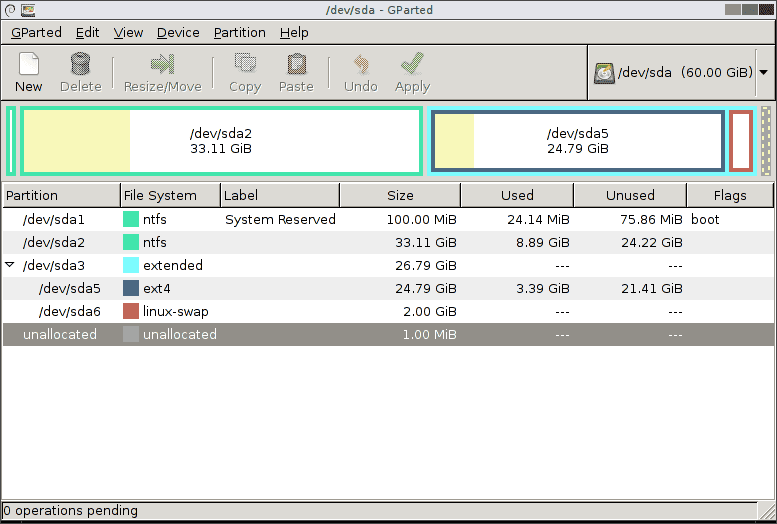
If you have any problems with the text-based Open-source Linux Partition Manager, this one is the right one for you. This disk partition manager comes with a graphical combination. You can easily detect the necessary partitions. Moreover, the tool has some advanced features. Gparted can work with multiple operating systems, including Windows.
As a result, you can make the necessary partitions even if you are an amateur in this arena. This free software can make some important commands, and it is even enabled to check the present partition conditions. You can delete unnecessary data from your disk, and there are fewer chances of data loss.
4. GNOME Disks
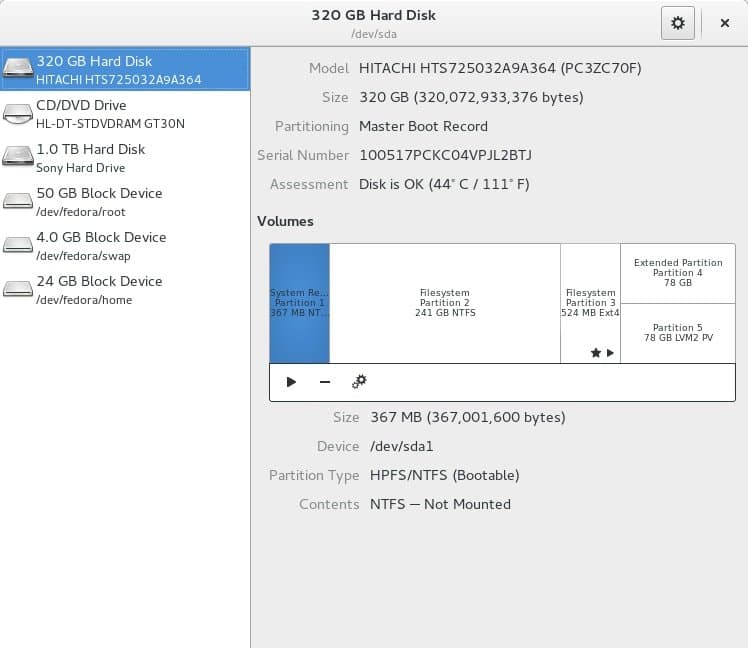
The Linux community also terms this software Gnome Disks Utility. This is a system utility tool for your core system. You can have some impressive options for this tool. It is armed with a S.M.A.R.T. monitoring system. The software is basically used to create partitions. You will also have the option of mounting and unmounting the partitions based on your needs.
This is mostly for advanced-level users. The updated version has some specific features. The users can repair file system damages and resize the partitions.
5. KDE Partition Manager
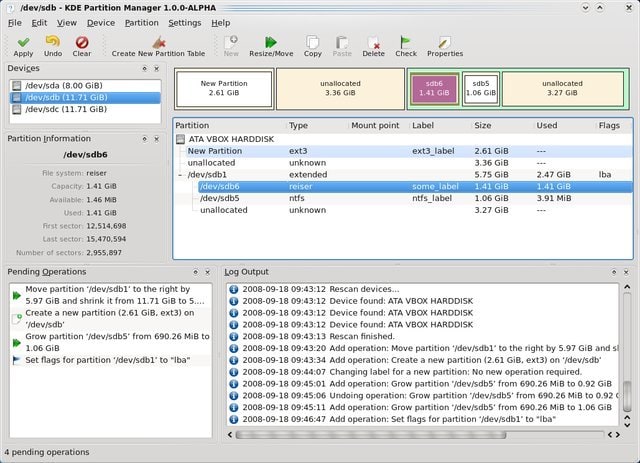
When you are seeking a simple Linux partition manager, this is the perfect tool for you. Managing disks has not been easier before. The tool comes with a graphical interface. As a result, you are able to see what exactly you are doing with the disk partition.
The tool has really an admiring desktop environment. The software allows you to do basic tasks like restoring partitions, copying, moving files, resizing partitions, etc. Besides, the tool is compatible with various extensions.
6. Palimpsest Disk Utility
Often, the tools used for Linux partitions can be used for several other purposes. And this is one of those. You can use this tool for benchmarking or monitoring purposes, too, in line with partition. The tool gained huge popularity for its simplicity in the user interface section.
Furthermore, the tool is loaded with a warning system that will inform you immediately about the condition of the partition so that you can take the necessary actions accordingly. Besides, you can run some self-tests. This certainly will help you to know the exact condition of the hard disk.
7. Qtparted
Qtparted is another wonderful tool for Linux partitioning. But unluckily, the complete development of the tool is still underway. Consequently, while applying, you might have some trouble partitioning with this particular tool. Only advanced users would be able to handle it as they know the pros and cons of this software. However, the overall performance of this tool while creating a partition is really praiseworthy.
8. Partmod
Partmod is a familiar tool for disk partitioning in the Linux system. This particular software can perform on several platforms. You can apply this tool to GPT disks too. The partitioning process becomes easier when you apply this tool to your device.
The interface shows the detailed conditions of the existing partitions, and based on the view, you can make your own decision. You can revise the partitions based on your needs and allocate spaces in each of your drives.
Final Words
Linux is one of the most reliable and fastest-growing platforms in the world. Hence, the necessity of the Linux Partition Manager cannot be denied at all. The Linux Partition Tool allows you to set the disk simply so that you can have enough space while working. Often, you might have trouble with your existing hard disk partitions.
The disks may need more space for ordinary use. The Open-source Partition Software provides the tools for you absolutely free. You just need to download them and install them on your devices. This is really a simple task.
Amateur people with Linux would greatly benefit if they used any of the aforementioned partition tools during the partitioning process. The application of each of the processes is easier and more user-friendly. Therefore, you can rely on the Linux Partition Manager without any second thought.
