Ubuntu Linux is a polished Debian-based Linux distro; however, you may start to experience some system lag days after installation. There are many reasons this might happen. If you want to speed up your Ubuntu desktop performance, then follow these simple tips and tweaks. These tips will help you smooth out your system performance so that you can do your regular tasks more easily. You don’t have to follow all of the tips, but even just a few of them will make a big difference in the overall performance of your Ubuntu system.
Tips To Speed Up Ubuntu Linux Performance
You may find lots of tweaks and tips on how to speed up Ubuntu Desktop Performance on the Internet. Some are safe, and some are risky. Here, I will be sharing only safe and stable tweaks because I believe that system stability and reliability are much more precious and important than gaining speed.
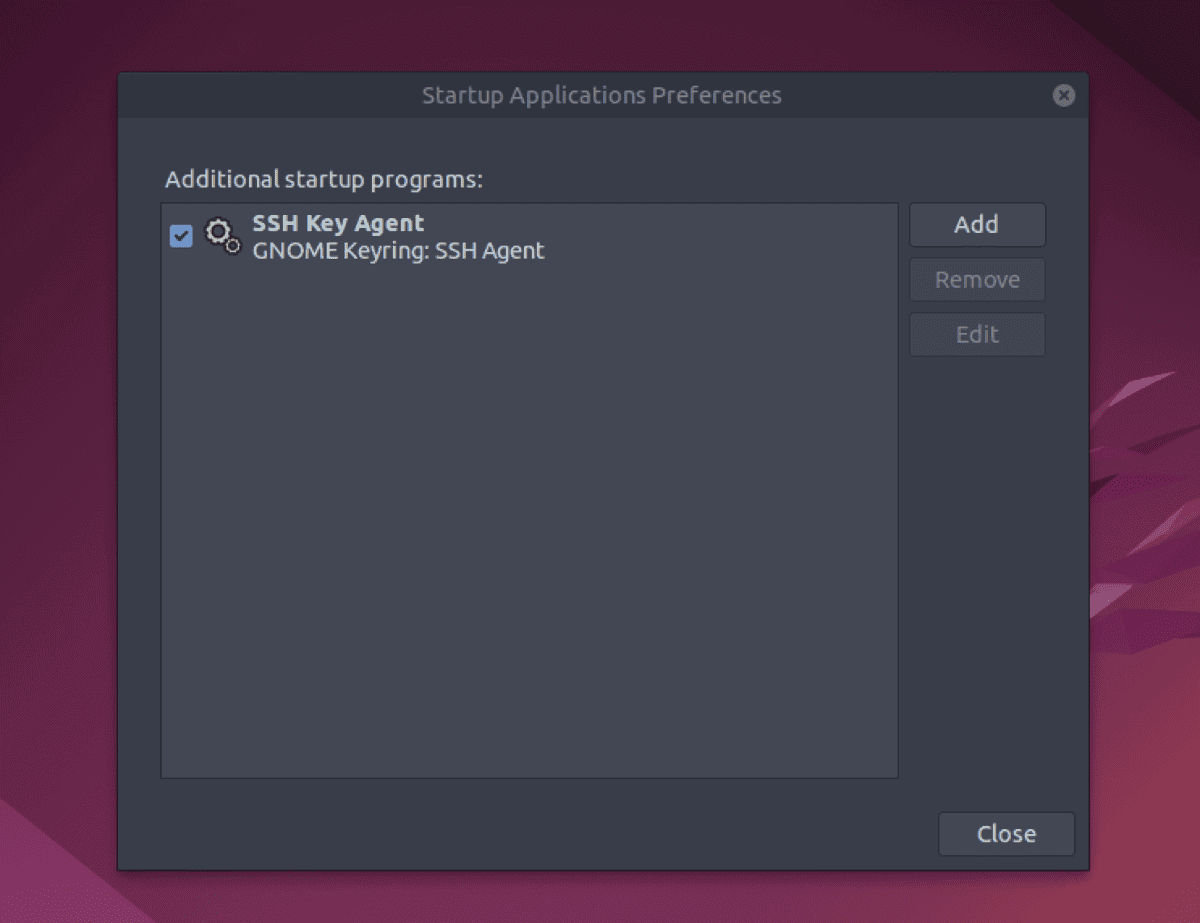
1. Manage Startup Applications
After installing fresh Ubuntu, your system seems fast and smooth, but over time, users intend to install lots of applications. Startup applications take up a huge resource while the system boots up, which makes the system slow and gives poor performance. So, on an Ubuntu system, it’s better to manage startup applications at the best level.
There are many applications, such as Bluetooth manager, email client, remote client, visual assistant, etc., that might not be necessary during startup. So, to reduce the startup application list, follow…
- Gnome Application Drawer >> Search for Startup >>Add/Remove/Edit as you like
2. Install Preload
Preload is a handy tool that runs in the system background and uses artificial intelligence to understand the behavior of the system user. This is how it loads the application very fast, depending on how often the user uses it. Follow the command from the Terminal to install preload in Ubuntu.
sudo apt install preload
3. Create a Swap Partition
If your machine has less RAM, you should create a swap partition during the initial Ubuntu installation. Normally, the Swap partition is double the size of the actual RAM. For example, if you have 2 GB of RAM, then the Swap Partition will be 4 GB in total size.
This partition will use your HDD as RAM to speed up the launching of applications and background processes. Do not create this Swap partition if you have more than 4 GB RAM.
If you forgot to make a Swap partition during Ubuntu installation, don’t worry! You can easily follow one of the many tutorials available online on how to do so.
4. Reduce the Default Grub Load Time
When a laptop starts up, the Grub screen displays options for dual-booting OSes or starting recovery mode. Usually, users have 10 seconds to choose. That means they must wait anywhere from 0 to 10 seconds or hit Enter to proceed. To reduce the time spent waiting on this screen, follow these instructions:
Run the following command.
sudo gedit /etc/default/grub
GRUB_TIMEOUT=10 to GRUB_TIMEOUT=2. This will make the Grub load time quicker, at only 2 seconds. To implement this change, run the following command.
sudo update-grub
5. Choose the Best Mirror for Software Updates
If you have a slow internet connection, this procedure will select the best server for updating the Ubuntu system.
Application Drawer >> Search for Software & Update >>Ubuntu Software Tab >>Select Best Server ( Download From Tab )
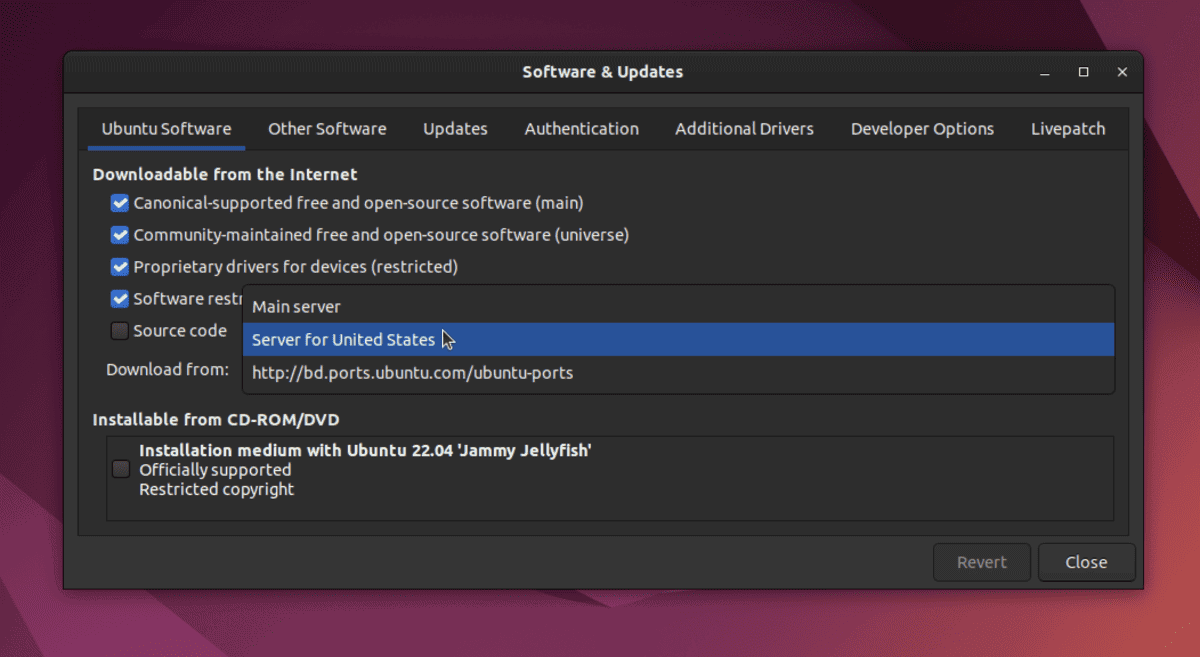
The system can determine which server is nearest to you by starting this test. This will help get updated files into your system more quickly during a software update or upgrade. Speeding up the Ubuntu system in this way enables it to install all new security bug fixes and missing drivers that are required.
6. Reduce Overheating
Overheating problems are very common on laptops. This makes the laptop run slow and gives poor performance. There is a very effective tool in the Ubuntu repository that can help to cool down your system, and that will make the Ubuntu system smoother and faster. After installing TLP, you do not need to configure anything. Rather, just run the command.
sudo apt update sudo apt install tlp tlp-rdw sudo tlp start
7. Use apt-fast instead of apt-get
Apt-get is an obvious command when you go for any software installation or update your Ubuntu system. Here, I would like to recommend you use apt-fast instead of apt-get, at least have a try, for a speedy update or downloading app packages simultaneously while using multiple connections. Install apt-fast via official PPA using the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable sudo apt update sudo apt install apt-fast
8. Use a Lightweight Desktop Environment
Ubuntu comes with a preinstalled Gnome desktop environment, which loads quite heavily onto the system. But you can always try to install another lightweight desktop environment ( like Xfce or LXDE) and see whether it can fulfill your requirements or not. I have a detailed tutorial on various desktop environments for Ubuntu Linux. You can check it sometimes.
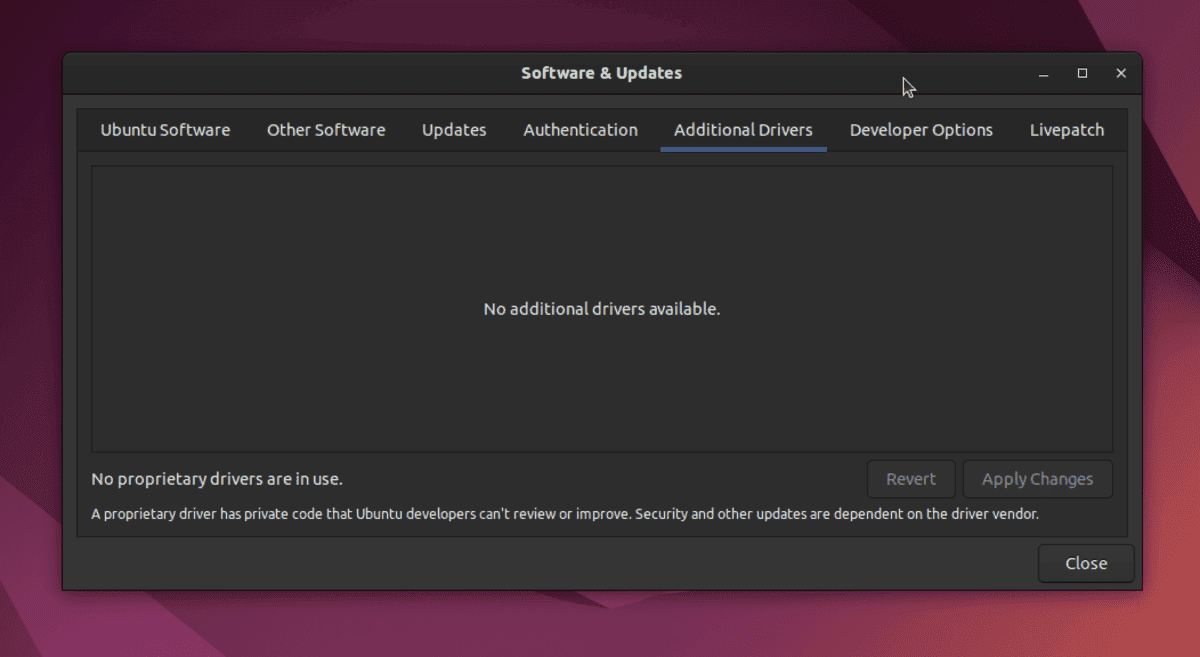
9. Enable Proprietary Drivers
If you want to access the newest Ubuntu games and engage in high-level graphical design, you must enable proprietary drivers. Modern Linux laptops and desktops have great processing power and graphics cards, but you won’t be able to utilize them to their fullest potential without these drivers. To install and see which ones are available for your hardware, go to Applications Overview >> Software & Updates >> Additional Drivers >> Install/Apply changes.
10. Use System Cleaner Apps on Your Ubuntu Linux
Just because your computer is running Ubuntu Linux doesn’t mean you can’t speed up its performance. In fact, a variety of System Cleaner apps are available on the market just for this purpose! With these apps, you can clean out unwanted files and folders in a flash so that your computer will be running faster than ever before.
So, if you’re looking for a way to speed up the performance of your Ubuntu Linux machine, be sure to check out these awesome System Cleaner apps! Now, that’s how you get the most out of your computer!
11. Remove Unnecessary Apps from Your Ubuntu Linux
Unnecessary applications can slow down your system. Go through the list of your installed apps and remove the ones that you no longer need or use. You can also use System Monitor Tools or “Top” to view the list of running applications and find out which ones are utilizing a lot of your system resources. You can then uninstall these unwanted apps to free up some space and memory usage on your computer.
12. Uninstall Unused Language Packages
If you don’t need other languages on your system, then uninstall them to free up some space and resources. You can do this from System Settings -> Region & Language -> Manage Installed Language. Here, you can select the language packages you don’t need and click on Uninstall.
13. Update Your System Regularly
Keeping your system up-to-date is very important in order to get the latest improvements and bug fixes released by Canonical (the maintainers of Ubuntu). To update your system, open the Software Updates app and click on Check. Then, follow the instructions to install any available updates. Or else you can run the following command in the Terminal:
sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade
14. Choose a Lightweight App over a Heavy one
If your computer is short on resources, then you can opt for lighter alternatives to different applications. For instance, use Firefox instead of Chrome or VLC instead of any other media player. Also, try to install lightweight themes and extensions that can help reduce system resource usage. This will help you run applications faster and more efficiently.
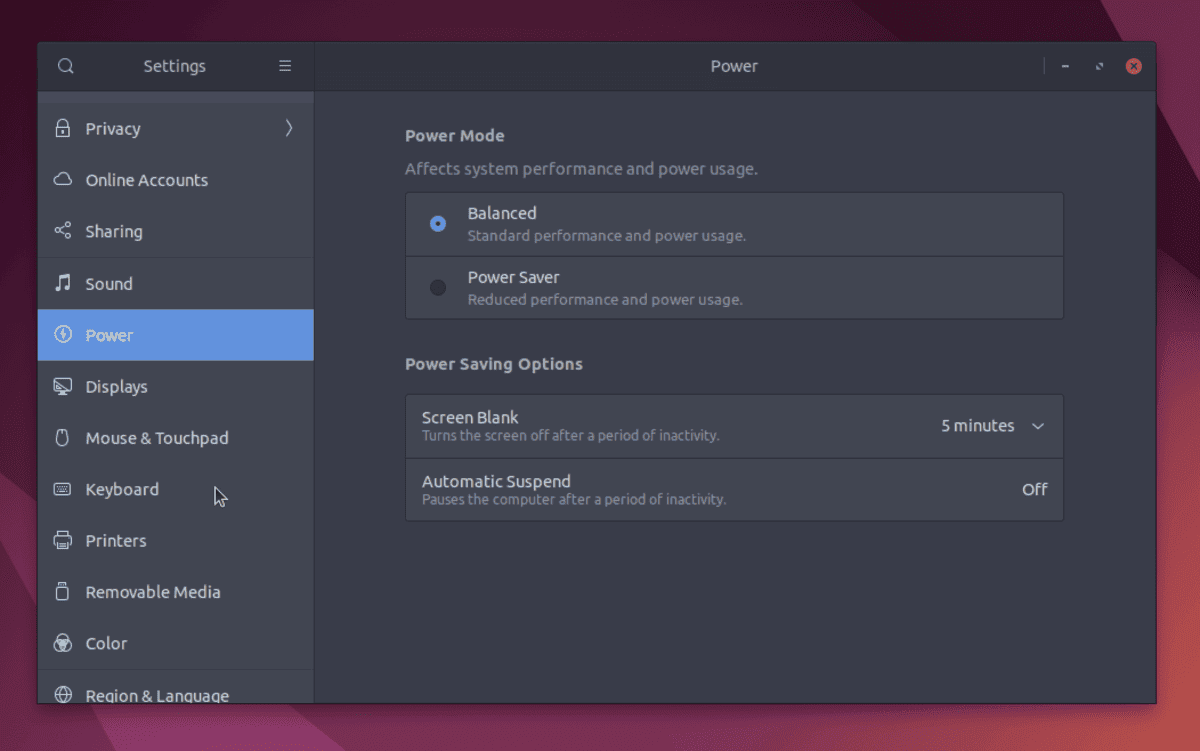
15. Optimise Your System Settings For Speed
There are some basic system settings that can be changed to improve system performance. Go to the System Settings and set the power settings to Balanced or Power Saving if you are running low on battery. The refresh rate can be adjusted under Settings >> Display. A high refresh rate will result in more power being used.
16. Disable Unnecessary Services
Services are applications that run in the background and can be used to manage certain system activities. But some of these services may not be necessary or useful for your system. To check the list of running services, open a Terminal and run the command:
sudo service --status-all
You can then disable any unwanted or unnecessary services with the command:
sudo service <service_name> stop
17. Clean up Ubuntu Linux
First of all, I like to focus on apt command. This command is the most powerful command in UNIX/Linux Terminal, which lets you do almost anything about software installation, uninstallation, downloads, etc., before doing anything; it makes a cache in your HDD consisting of all downloaded data.
So it gets bigger and bigger after a certain of time. This makes the system slow and sluggish. To remove all those caches from your system HDD, run the following command.
sudo apt clean
Don’t get worried. It does not delete any installed application from your system.
Now, I will highlight the application “dependencies.” When an application is installed, other related small applications are also installed to have full functionality. But if you uninstall the application, the dependencies or small subsidiary applications will not be removed.
So, it creates junk files on the HDD and slows the system. To clean up all these unnecessary packages or unwanted “Dependencies” from the system, run the command.
sudo apt autoremove
Final Thought
All these above tips and tweaks are given based on Ubuntu’s latest version, but these tips also can be used in all other old versions of Ubuntu. Moreover, other Linux distros that are based on Ubuntu, like elementary OS, Linux Mint, etc, can similarly apply these Speed Up Ubuntu tips and tweaks. These tips and tweaks help you significantly maintain and speed up your Ubuntu desktop performance.
Do you have any tweaks that helped speed up the Ubuntu system? Did you like all the above tweaks? Please share your views, questions, and suggestions in the comment section below.

Well, I really appreciate existence of ZRAM project. First I’ve tried it many years ago on Lubuntu installed on weak laptop (yes, it was weak even those days – it had only 512 MB of RAM). And even few Firefox windows made its performance horrible. The reason was simple – low memory plus contemporary web-browser caused swapping to disk (and the performance of 5400 SATA disk is far from SSD or NVMe). And… ZRAM saved me! The difference was unexpectedly noticeable.
In Ubuntu it’s enough just to install small package zram-config and that’s it – command “sudo apt-get install zram-config”.
To check if it working run the command “swapon -s” – it will show all the active SWAP partitions.
FYI – I’ve a very extensive and successful experience with ZRAM – I use it for many years on my home desktop and laptop, on production servers, on virtual machines – and I’ve NEVER experienced any troubles with it. Also I’ve never felt any additional CPU load – it seems, that LZ4 algorithm is very optimized and lightweight on CPUs (both Intel and AMD). So this tweak is time-proved as 100% safe for me.
Well, sorry for this huge comment, but I would suggest to change the recommendation № 4 (concerning the SWAP partition) to use ZRAM SWAP instead.
got this when attempting to install the Gui configuration for tlp. Help?
steve@Studio:~$ gksu lmt-config-gui
Command ‘gksu’ not found, did you mean:
command ‘gosu’ from deb gosu
command ‘ksu’ from deb heimdal-clients
command ‘ksu’ from deb krb5-user
ey
Try: sudo apt install
Thanks for handy ones – several are part of my routine set up for Mint now. I’d throw in a major slug factor for LibreOffice, which is Java (OpenJDK), only required for templates and use of Base. Unchecking Java in the upper left of pop up of LibreOffice Tools / Advanced dramatically speeds the whole suite up.
Open JDK can then be deleted from the system:
sudo apt-get remove openjdk*
to restore it with LibreOffice support:
sudo apt-get install default-jre libreoffice-sdbc-hsqldb
“To clean up unnecessary packages or unwanted Dependencie: sudo apt-get autoremove”
a bit confusing. I thought apt-get installs software. But it sounds like you’re saying this command executes the autoremove process.
Do i have to run this command every time i install or remove a package? You didn’t say.
thx
Hello Johny, thanks for the comment. Many a time, we install or remove various software, especially when we first install any Linux distros. This above-mentioned command, you should use to remove any unattended dependencies that remain into the system after uninstalling any specific software or a group of applications. Apparently, this command cleans up the system from any unwanted software dependencies.
You only need autoremove after removing software, when you install software it installs these extra add ons called dependencies, when you remove it sometimes the dependecies are kept and not needed, sudo apt autoremove removes these uneeded dependancies to free up disk space
E: Unable to locate package apt-fast, means it does not work in Ubuntu 14.10, why?
9. Use apt-fast instead of apt-get
Apt-get is an obvious command while you go for any software installation or update your Ubuntu system. Here I would like to recommend you to use apt-fast instead apt-get, at least have a try, for a speedy update or downloading app packages simultaneously while using multiple connections. Install apt-fast via official PPA using the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install apt-fast
Fast and fustrating 🙂
Oh, and I forgot to mention that the repository for the tlp does as well not work for the old version, so there is no way to cool down the desktopwhen Ubuntu 14.10 is instaed, but an external USB-fan.
8. Reduce Overheating ???
Overheating problem is very common on laptops. This makes the laptop run slow and gives poor performance. There is a very effective tool in Ubuntu repository, which can help to cool down your system, and that will make the Ubuntu system smooth and faster. After installing TLP, you need not do any configuration rather just run the command.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:linrunner/tlp
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install tlp tlp-rdw
sudo tlp start
Dear sir. All these tips mentioned here are not checked on Ubuntu 14.10 but on latest Ubuntu, it definitely works.
Personally I use “uCareSystem”. This app is a must for every Ubuntu and derivatives
thanks for the tip….gotta love simple programs
I personally prefer Stacer with a beatiful GUI
fans are not working and dell inspiron 7567 is HOT inspite of installing tlp. Nvidia drivers crash the system and i have to reinstall the OS when i try and use them, everything turns grey and the system locks up, the iphone won’t mount, can’t play overwatch because i couldn’t get wine to load. There is more I’m just back in win10 right now so the laptop is cool. This is really a pain in the neck to have to try this hard and make it work I want to run ubuntu I have never tried another desktop I love compiz and emerald which on the upside are working im tired or reinstalling. I’m sick of the snarky answers they post on Ubuntu forums and just googling endlessly. Any suggestgions?